


The classical age in India began with the Guptas and the resurgence of the north during Harsha's conquests around the 7th century, and ended with the fall of the Vijayanagar Empire in the South, due to pressure from the invaders to the north in the 13th century. This period produced some of India's finest art, considered the epitome of classical development, and the development of the main spiritual and philosophical systems which continued to be in Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism. King Harsha of Kannauj succeeded in reuniting northern India during his reign in the 7th century, after the collapse of the Gupta dynasty. His kingdom collapsed after his death.
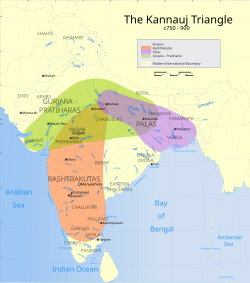
From the 7th to the 9th century, three dynasties contested for control of northern India: the Pratiharas of Malwa, the Palas of Bengal and the Rashtrakutas of Deccan. The Sena Empire would later assume control of the Pala Empire, and the Pratiharas fragmented into various states. These were the first of the Rajputs, a series of kingdoms which managed to survive in some form for almost a millennium until Indian independence from the British. The first recorded Rajput kingdoms emerged in Rajasthan in the 6th century, and small Rajput dynasties later ruled much of northern India. One Rajput of the Chauhan clan, Prithvi Raj Chauhan, was known for bloody conflicts against the advancing Islamic Sultanates. The Shahi dynasty ruled portions of eastern Afghanistan, northern Pakistan, and Kashmir from the mid-seventh century to the early eleventh century.
The Chalukya Empire ruled parts of southern and central India from 550 to 750 from Badami, Karnataka and again from 970 to 1190 from Kalyani, Karnataka. The Pallavas of Kanchi were their contemporaries further to the south. With the decline of the Chalukya empire, their feudatories, Hoysalas of Halebidu, Kakatiya of Warangal, Seuna Yadavas of Devagiri and a southern branch of the Kalachuri divided the vast Chalukya empire amongst themselves around the middle of 12th century.
The Chola Empire at its peak covered much of the Indian Subcontinent and Southeast Asia. Rajaraja Chola conquered all of peninsular South India and parts of the Sri Lanka. Rajendra Chola's navies went even further, occupying coasts from Burma (now Myanmar) to Vietnam,[46] the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep, Sumatra, Java, Malaya in South East Asia and Pegu islands. Later during the middle period, the Pandyan Empire emerged in Tamil Nadu, as well as the Chera Empire in Kerala. By 1343, all these dynasties had ceased to exist giving rise to the Vijayanagar empire.
The ports of South India were involved in the Indian Ocean trade, chiefly involving spices, with the Roman Empire to the west and Southeast Asia to the east.[47][48] Literature in local vernaculars and spectacular architecture flourished till about the beginning of the 14th century when southern expeditions of the sultan of Delhi took their toll on these kingdoms. The Hindu Vijayanagar dynasty came into conflict with Islamic rule (the Bahmani Kingdom) and the clashing of the two systems, caused a mingling of the indigenous and foreign culture that left lasting cultural influences on each other. The Vijaynagar Empire eventually declined due to pressure from the first Delhi Sultanates who had managed to establish themselves in the north, centered around the city of Delhi by that time.

No comments:
Post a Comment